Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children. It is a natural reflex that offers comfort and security, often assisting babies in self-soothing and falling asleep. Thumb sucking usually starts in infancy, although it can happen even before birth since ultrasounds have shown fetuses sucking their thumbs. Most children outgrow this tendency between the ages of two and four. However, if thumb sucking continues beyond this age, it can be detrimental to dental health and development.
The transition from a comforting behavior to a potential dental issue occurs when the habit continues as the child’s permanent teeth emerge, typically around the age of six. Prolonged thumb sucking can cause severe dental and orthodontic issues that may necessitate professional treatment.
Effects of Thumb Sucking on Dental Health
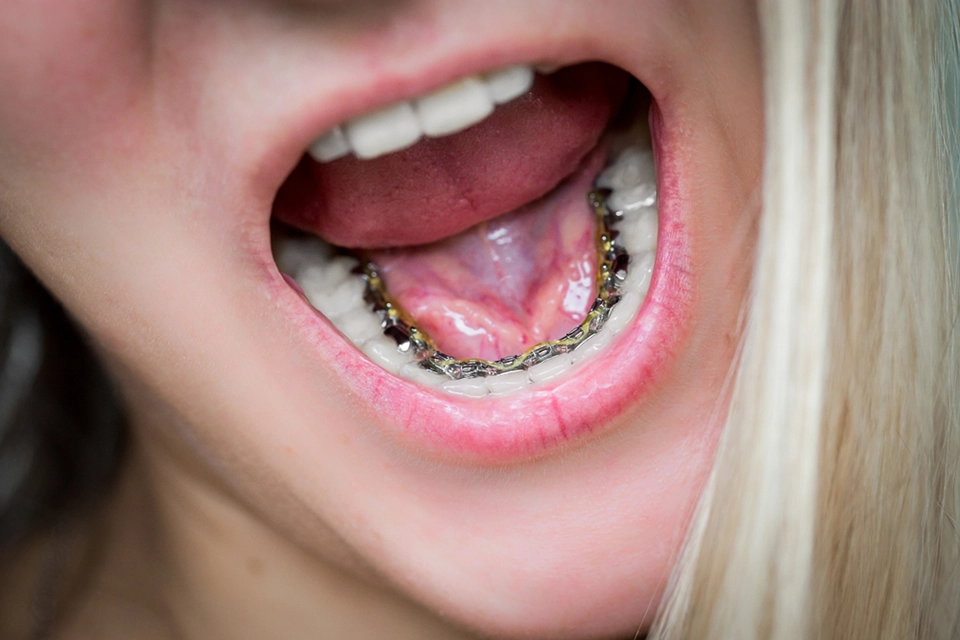
- Open Bite: One of the most visible consequences of excessive thumb sucking is an open bite. This condition occurs when the front teeth do not meet when you close your mouth. This gap can make chewing and speaking difficult and cause self-esteem issues due to the appearance of the teeth.
- Overbite: An overbite is defined by an abnormal protrusion of the top front teeth. This happens because the persistent pressure of the thumb on the top teeth pushes them forward. In addition to potentially increasing the risk of injury to the protruding teeth, an overbite can result in difficulties with biting and chewing.
- Crossbite: Prolonged thumb sucking can also cause a crossbite, a condition in which the upper teeth fall inside the lower teeth while the mouth is closed. This jaw misalignment can create uneven wear on the teeth, resulting in jaw pain and dysfunction.
- Changes in Jaw Shape: A long-term structural change may result from the continuous pressure and sucking action that can change the shape of the jaw and palate. These alterations may affect the overall alignment of the teeth, necessitating extensive orthodontic therapy.

How to Stop Thumb Sucking?
- Preventive Measures: Preventing the tendency from becoming ingrained in younger children can save them a lot of trouble later. Positive reinforcement is a practical approach; praising and rewarding your child for not sucking their thumb can help them to stop. Introducing other comfort objects, like a favorite blanket or stuffed animal, might also assist in shifting their need for soothing away from their thumb.
- Interventions for Persistent Thumb Sucking: There are many solutions available to assist children who continue to engage in the behavior. There are bitter-tasting nail solutions available that make thumb-sucking unpleasant. To physically stop thumb sucking and assist in breaking the habit, you can use orthodontic devices such as thumb guards. If these techniques do not work, it may be time to seek professional assistance. A pediatric dentist or orthodontist can offer advice and may suggest custom treatments to stop thumb sucking.
- Corrective Techniques: Once thumb sucking has been stopped, it is essential to address any dental issues that have arisen. Braces and other orthodontic procedures can treat open bites, overbites, and crossbites. The jaw or palate may require additional treatments to achieve the desired shape. Early intervention is critical for reducing the treatment needed and ensuring the best possible outcome for your child’s dental health.
Consulting Professionals
Knowing when to seek professional assistance is essential for dealing with thumb sucking-related dental issues. If your child’s thumb sucking continues after age 4, or if you notice any changes in their bite or dental alignment, it’s essential to see a pediatric dentist or orthodontist. During a professional evaluation, the dentist will examine the severity of the dental problems caused by thumb sucking and recommend appropriate treatment. This evaluation might include X-rays, a physical examination, and a discussion of your child’s habits and behavior.
In conclusion, while thumb sucking is a natural and common habit in young children, it is critical to monitor its persistence and impact on oral health. Guide your child towards improved dental health and prevent long-term complications by understanding the potential issues and how to intervene. If you are concerned about your child’s thumb sucking habit, contact the professionals at Zara Dental in Houston, Texas, for expert advice and treatment options customized to your child’s specific needs.