What Exactly Is a Mouth Ulcer?
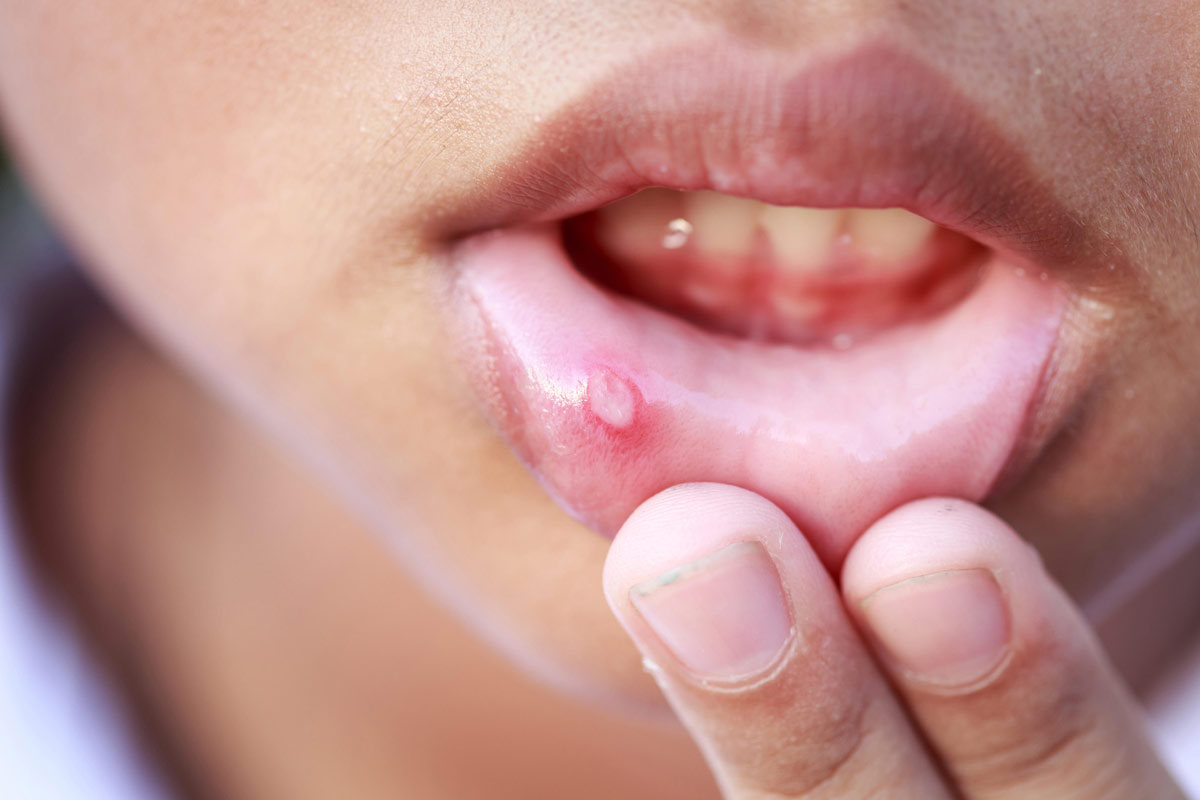
A mouth ulcer, is an extremely painful sore that forms inside the mouth. Mouth ulcers are a widespread condition affecting people of all ages, although teenagers and young adults are more likely to develop them.
Mouth ulcers come in various forms, each with its causes and traits. However, the following are the most prevalent kinds of mouth ulcers:
Types
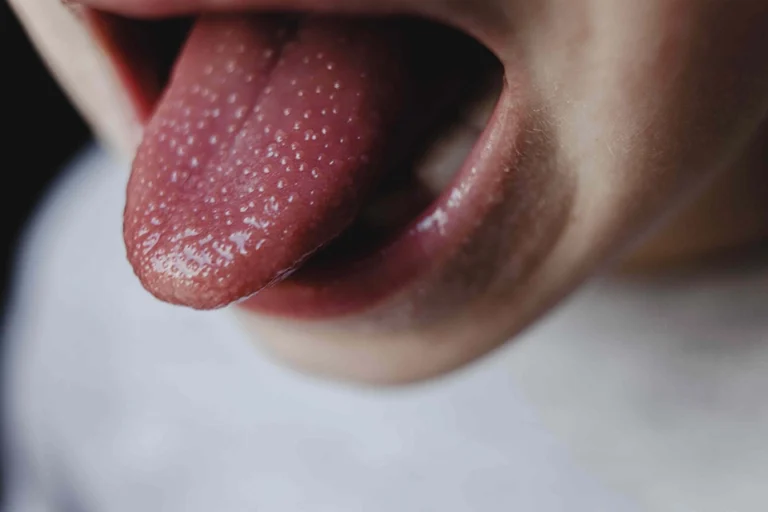
Canker Sores
They are small, round, or oval sores that form inside the mouth, generally on the cheeks, lips, tongue, or gums. Moreover, they usually are white or yellow in the middle with a red border. Canker sores are not contagious and usually heal within a week or two.
Cold Sores
The herpes simplex virus, often known as fever blisters, causes cold sores. Moreover, they are small, fluid-filled blisters that form on or around the lips. Additionally, cold sores are contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with blister fluid. They usually heal in 7-10 days.
Oral Thrush
A fungal infection known as oral thrush can result in white, creamy patches appearing on the tongue, cheeks, and roof of the mouth. Infants, older people, and those with compromised immune systems are most susceptible to it.
Oral Cancer
A mouth ulcer may occasionally indicate oral cancer. It is crucial to visit your dentist or doctor for an evaluation if a mouth ulcer does not go away in 2-3 weeks or is accompanied by additional symptoms like swelling, redness, or trouble swallowing.
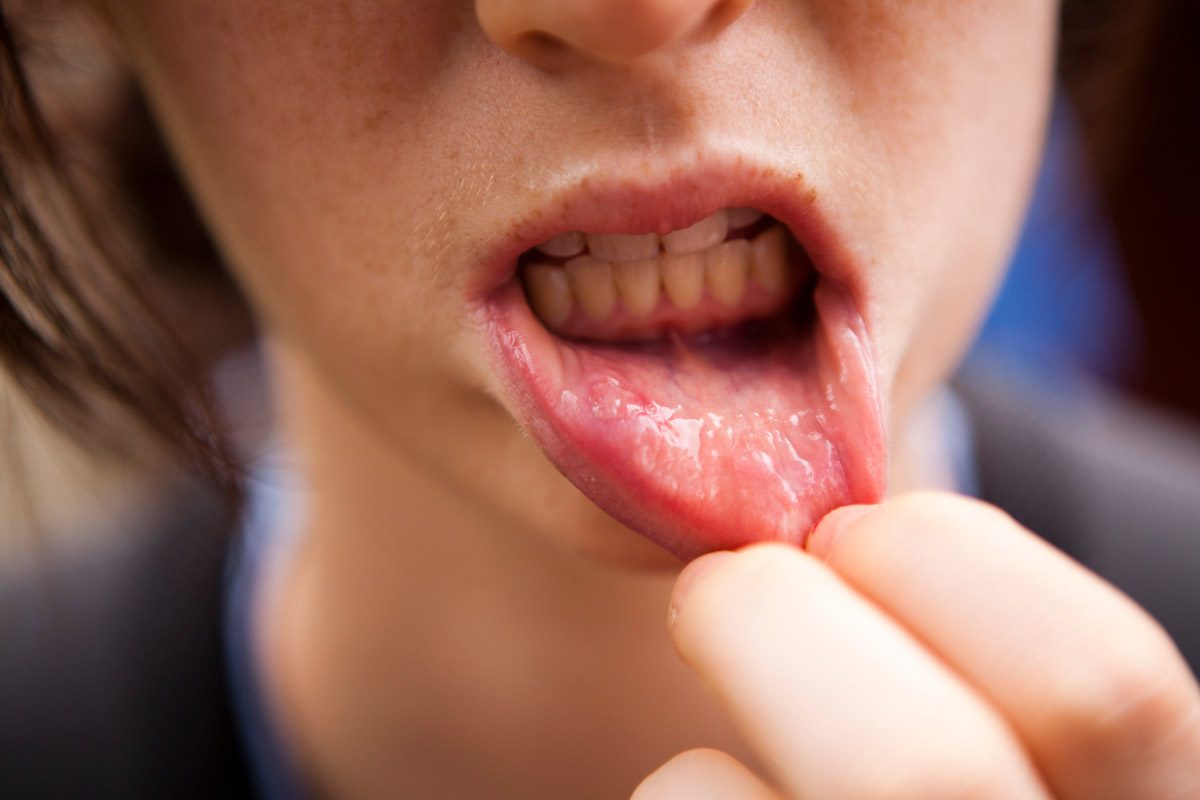
Symptoms of a Mouth Ulcer
The symptoms of a mouth ulcer vary based on the type and location of the ulcer.
However, in general, the most typical signs of a mouth ulcer include:
- Discomfort or Pain: Mouth ulcers can be excruciatingly unpleasant, mainly when eating, drinking, or talking.
- Inflammation or Redness: The area surrounding the ulcer may be red, swollen, or irritated.
- White or Yellow Center: Some ulcers may have a white or yellow center with a red border.
- Raised Bumps or Lumps: Some ulcers may resemble raised bumps or lumps on the inside of the mouth.
- Difficulty Eating or Drinking: Mouth ulcers can be uncomfortable, especially on the tongue or within the cheeks.
- Fever: If a bacterial or viral infection brings on a mouth ulcer, this condition may also be accompanied by a fever.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Neck lymph nodes may swell due to an infection-related mouth ulcer.
How Is a Mouth Ulcer Treated?
Dentists may use different treatments for mouth ulcers depending on the type and severity of the ulcer. Most mouth ulcers heal within 7-10 days and do not necessitate treatment.
There are, however, some medical procedures that might lessen discomfort and hasten the healing process.
The following are some common treatments for mouth ulcers:
- Over-the-counter Medications: Painkillers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help to reduce inflammation and relieve discomfort.
- Oral Gels or Creams: You can apply topical drugs, such as benzocaine, directly to the ulcer to ease pain and discomfort.
- Mouthwash: Using an antiseptic mouth to rinse your mouth may help reduce irritation and prevent infection.
- Steroid Medications: Your doctor might occasionally recommend a steroid medication like prednisone to reduce inflammation and accelerate healing.
- Nutritional Supplements: Supplements may be advised if there is a nutritional shortage that is the root of the ulcers, such as a lack of iron or vitamin B12.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: If certain foods or beverages are causing the ulcers, eliminating them may help to prevent future outbreaks.
Practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly to reduce your risk of developing mouth ulcers. Call us at Zara Dental in Houston, Texas if your mouth ulcer doesn’t heal in two to three weeks or if you experience other symptoms, such as swelling, redness, or difficulty swallowing.